While we are often advised to stop consuming as much sugar, it isn’t the easiest thing in the world to do. This is because of how our taste buds work. When they detect sugar (fructose, sucrose, maltose, glucose, etc), the “sweet” signal is sent to our brain which then gets processed by our brain’s “reward system”. This is one of the reasons why we find it so hard to give up on some of the sugary treats we love. The following describes your brain activity when there is an imbalance of sugar in your system.
Similarities Between Sugar and Cocaine Consumption
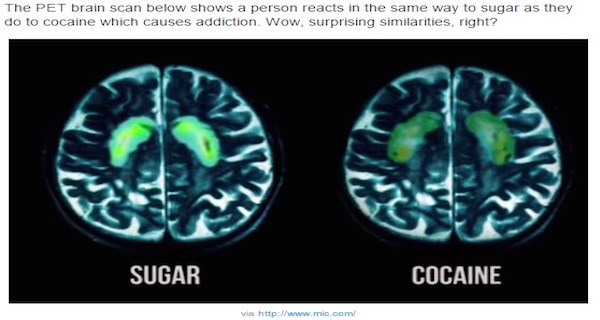
PET brain scans have proven that the way a person reacts when sugar is in their system, is the same as the reaction to cocaine. This leads to an addiction. Quite the similarity.
Dopamine
Dopamine is a chemical which is produced in the same part of the brain that is connected with the “reward system”. The red areas of the scan below show where dopamine is present – more in a “normal” brain. When we eat something that we find delicious and feel rewarded, our dopamine levels spike.
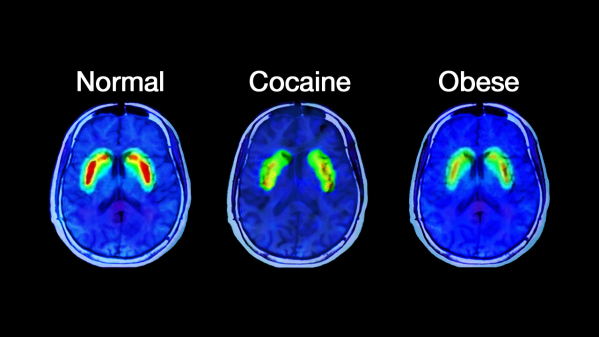
The only way an addict can get a dopamine spike is by anticipating a reward, compared to the actual experience. If an addict eventually has that reward, their dopamine levels will not spike as they have already flooded their brain with dopamine by just anticipating the reward.
Comparing Normal and Addict Brains
Let’s observe the dopamine receptors shown in each of the brains, both the normal and the addict brains. The images below in the bottom row are from non-addicted individuals and the images shown in the top row are from addicted individuals.
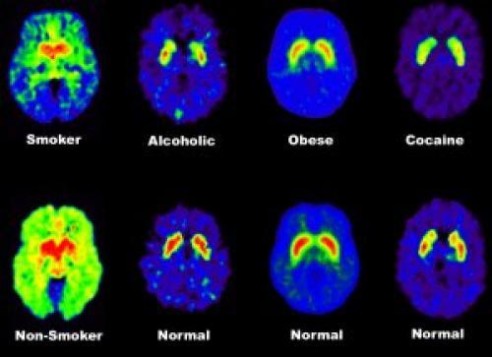
Notice how the brains of those with an addiction disorder have a lower dopamine receptor count? This means that the dopamine signals sent between the brain cells are significantly weaker. Their “reward system” is less sensitive compared to a normal brain.
This is thought to be because the brains of addicts over-consume what they are addicted to, making them less sensitive. Overall, having a sugar addiction is very similar to having a smoking, alcohol, or cocaine addiction.
Over Consuming Sugar
Just as the PET brain scans showed us, cocaine and sugar can be incredibly bad for you. Once they are consumed in very large amounts, your body will not only be less sensitive to the effects they have, but over consuming on sugar can lead to obesity and a life of diabetes. Sugar is also known to have an impact on your metabolism, as well as your brain function. Consuming too much sugar can lead to heart disease, cancer, and has been known to even cause wrinkles.
Diabetes
The Centers for Disease Control has estimated that by the year 2050, the number of Americans who have diabetes will have at least doubled, and possibly even tripled. Another study which was published in the Population Health Metrics expects that there will be between a 21% and 33% increase in the amount of Americans affected by diabetes.
Cutting Down on Sugar
A productive method to cutting down on your sugar is to do your best to remove the visibility of sugary snacks from your home. While you can try your best to not buy them, a lot of people tend to continue to buy sugary foods just out of habit. Put your unhealthy foods in cupboards and drawers, and instead place fruit bowls out in the open to tempt your mind in the right direction.
